- Introduction
- Service Hours & Contact
- Doctors
- About Nuclear Medicine & PET
- Radionuclide Therapy
- Leaflets
- Health Education
Nuclear Medicine & PET Centre
Nuclear Medicine & PET Centre, aims at providing patients with comprehensive and highest quality Positron Emission Tomography, Nuclear Medicine and Radionuclide Therapy services.
In year 2001, the Hospital began to provide Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography (PET-CT) services. The Nuclear Medicine services was established in 2010. Over the years, both centres have been providing quality diagnostic services detecting functional and physiological disorder of human organs.
Inaugurated in 2014, Nuclear Medicine & PET Centre was established by merging the Positron Emission Tomography and Nuclear Medicine services to fully optimize the medical equipment. Equipped with the best in class instruments, the Nuclear Medicine & PET Centre provides top quality, accurate clinical imaging, and non-imaging diagnostic services as well as Radionuclide Therapy.
Our centre is equipped with a state-of-the-art digital PET scanner – GE Discovery MI Gen 2, dedicated to delivering comprehensive and high-quality PET imaging services to our patients. Compared to previous analog PET scanners, this next-generation digital PET scanner significantly improves detection sensitivity, allowing for up to a 50% reduction in radiation exposure for patients. Additionally, the digital detectors substantially enhance image resolution, enabling more precise detection of small and early abnormalities.
Scope of Services
- Nuclear Medicine
- Positron Emission Tomography – Computed Tomography (PET-CT)
- Radionuclide Therapy (including Iodine-131 for thyrotoxicosis, Iodine-131 for thyroid cancer ablation, Lutetium-177 PSMA for Prostate Cancer, Lutetium-177 for neuroendocrine tumor.)
Nuclear Medicine & PET Centre
| Monday – Friday | 9:00am – 5:00pm |
| Saturday | 9:00am – 1:00pm |
| Sunday and Public Holidays | Closed |
For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at:
Our centre will also provides service at HKBH’s own Medical Centre — HKBH East Kowloon Medical Centre (EKMC). For more details, please contact us at: (By appointment only)
PET Scan Centre
| Monday – Friday | 9:00am – 5:00pm |
| Saturday | 9:00am – 1:00pm |
| Sunday and Public Holidays | Closed |
For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at:

What is Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear Medicine is a specialized field of clinical medicine that employs unsealed radioactive substances, known as Radiopharmaceuticals, to diagnose and treat various diseases. These radiopharmaceuticals are designed to target specific cells or molecules, enabling precise diagnostic imaging and targeted treatment at the cellular or molecular level.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging in Nuclear Medicine involves administering a small amount of radiopharmaceuticals to patients, usually through intravenous injection or oral ingestion. After binding to specific cells or molecules, these radiopharmaceuticals emit radioactive signals (e.g. γ rays) that are detected by advanced imaging systems, including Gamma Camera & SPECT-CT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography-Computed Tomography) and PET-CT (Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography). By visualizing metabolism of radiopharmaceuticals within the body, these technologies allow early disease detection before structural changes occur and aid in functional assessment of abnormalities identified on conventional imaging methods.


What are SPECT-CT and PET-CT?
SPECT-CT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography-Computed Tomography) and PET-CT (Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography) are hybrid imaging modality that incorporates functional or metabolic assessment with structural assessment. The SPECT or PET scan demonstrates functional or metabolic abnormalities that occur in disease processes, while the CT scan localizes the anatomical sites of pathology and delineates the corresponding structural changes.
These imaging modalities are non-invasive procedures with no major side effects or discomfort on patients. Most radiopharmaceuticals have short half-lives and rapid metabolism. Therefore, the radiation dose from these imaging modalities to patients is at a very safe level.
Different examinations may have their own preparations and precautions. An instruction sheet will be provided to patients on the relevant details.
Common Indications of Conventional Nuclear Medicine Procedures (Gamma Camera & SPECT-CT):
-
Cardiology
- Diagnosis of ischaemic heart disease
- Assessment of myocardial ischaemia from known coronary artery stenosis
- Pre-operative assessment before major surgery
-
Endocrinology
- Differentiation between causes of hyperthyroidism
- Localization of hyperfunctioning parathyroid glands in hyperparathyroidism
- Evaluation of adrenal tumours
-
Gastroenterology
- Localization of gastrointestinal bleeding source
-
Neurology
- Evaluation of Parkinsonism
-
Nephrology & Urology
- Evaluation of renal function, urinary tract obstruction and renal scarring

GE NM/CT 870 DR
SPECT/CT Scanner

Stress / rest myocardial perfusion scintigraphy identifies significant reduction in blood flow to heart muscle due to underlying coronary artery stenosis
Common Indications of PET-CT
-
Oncology
- Localization of primary cancer site
- Differentiation between benign and malignant tumour
- Staging of cancer
- Evaluation of treatment response
- Surveillance for cancer recurrence
-
Cardiology
- Evaluation of myocardial viability
-
Neurology
- Evaluation of dementia (e.g. Alzheimer’s disease) and Parkinsonism
-
Inflammation and infection
- Localization of source for pyrexia or sepsis of unknown origin

GE DISCOVERY MI GEN2
PET-CT scanner
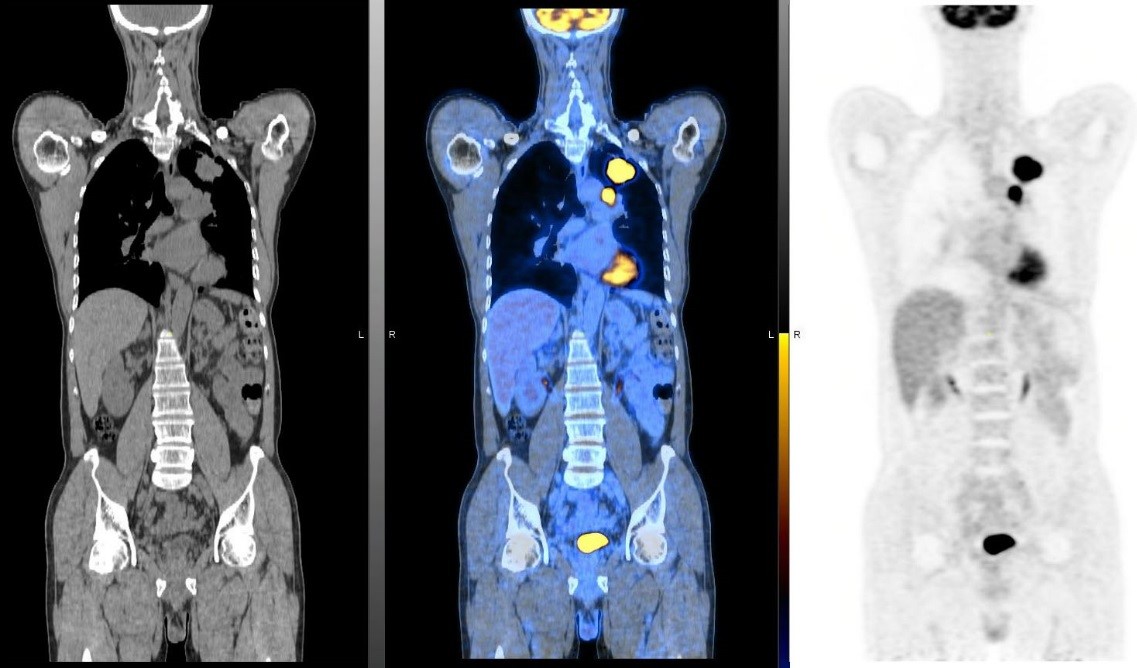
PET-CT shows lung cancer with nodal metastases
Radionuclide Therapy
In addition to diagnostic imaging, Nuclear Medicine also provides targeted treatment options for certain cancers through Radionuclide Therapy. In particular, the same molecules employed in diagnostic imaging are engineered as the carrier for subsequent therapy. These molecules precisely deliver the therapeutic high-energy radioactive particles (e.g. β particles) to diseased sites identified on diagnostic imaging, while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. This integrated therapeutic and diagnostic approach, known as Theranostics, creates a personalized and effective management plan tailored to each patient’s unique condition.
Common Types of Radionuclide Therapy
-
Iodine-131 (131I):
- For hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer
-
Lutetium-177 (177Lu)
Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) Radioligand Therapy (RLT):- For prostate Cancer
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT):
- For neuroendocrine tumour

Multiple metastases detected on 18F-PSMA PET

Multiple metastases targeted by 177Lu-PSMA radioligand therapy

